Ten quick tips for biomarker discovery and validation analyses using machine learning
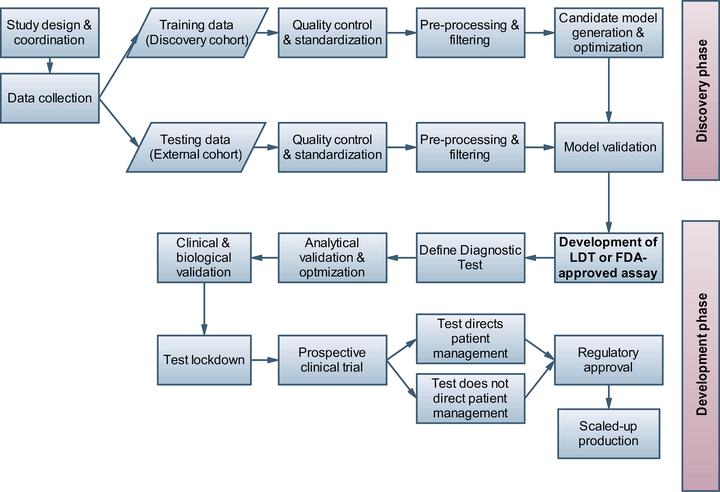 Image credit: From Diaz-Uriarte R, Gomez de Lope E et al.
Image credit: From Diaz-Uriarte R, Gomez de Lope E et al.
Abstract
High-throughput experimental methods for biosample profiling and growing collections of clinical and health record data provide ample opportunities for biomarker discovery and medical decision support. However, many of the new data types, including single-cell omics and high-resolution cellular imaging data, also pose particular challenges for data analysis. A high dimensionality of the data in relation to small numbers of available samples (often referred to as the p » n problem), influences of additive and multiplicative noise, large numbers of uninformative or redundant data features, outliers, confounding factors and imbalanced sample group numbers are all common characteristics of current biomedical data collections. While first successes have been achieved in developing clinical decision support tools using multifactorial omics data, e.g., resulting in FDA-approved omics-based biomarker signatures for common cancer indications [1], there is still an unmet need and great potential for earlier, more accurate and robust diagnostic and prognostic tools for many complex diseases. Here, we provide a set of broadly applicable tips to address some of the most common pitfalls and limitations for biomarker signature development, including supervised and unsupervised machine learning, feature selection and hypothesis testing approaches. In contrast to previous guidelines discussing detailed aspects of quality control, statistics or study reporting, we give a broader overview of the typical challenges and sort the quick tips to address them chronologically by the study phase (starting with study design, then covering consecutive phases of biomarker signature discovery and validation, see also the overview in Fig 1). While these tips are not comprehensive, they are chosen to cover what we consider as the most frequent, significant, and practically relevant issues and risks in biomarker development. By pointing the reader to further relevant literature on the covered aspects of biomarker discovery and validation, we hope to provide an initial guideline and entry point into the more detailed technical and application-specific aspects of this field.